Orthopedic Surgery
Rotator cuff tears
A rotator cuff tear is the most common cause of chronic pain in the shoulder in adults. It refers to a rupture of the shoulder tendon due to inflammation or degeneration of the rotator cuff that surrounds the shoulder joint. The pain worsens when you raise your arm or when you sleep on the back. In cases of complete rupture, you can not lift your arm at all. Through an MRI scan, the muscle from the torso comes connected to the shoulder and turns into a tendon, in which you can see that the muscle is torn and detached. That is supposed to adhere to the humerus of the arm.

Treatment of rotator cuff tears
-
Non-surgical treatment
In case of partial rupture, muscle strength exercise for functional recovery can be performed along with injection and medication. After inflammation is relieved using anti-inflammatory injection, block injection, or pain reliever injection, you can start exercise to restore its functions. Even if the pain has lessened, the rupture itself remains as it is. You should be careful as the rupture can be worse.
-
Arthroscopic surgery
Except for minor ruptures, surgical treatment is required. The treatment with arthroscopic sutures can help recovery, with the torn rotator cuff sutured. If the ruptured rotator cuff is left unattended for a long period of time, reconstruction technique using artificial tendons is required. If the secondary arthritis happens due to rotator cuff tear, reverse total shoulder arthroplasty can be necessary.
Calcific tendinitis
Calcium tendinitis causes severe pain when the shoulder tendon becomes inflamed after calcified as the part with inflammation hardens like a stone. The exact cause is not confirmed, but it is reported that the tendon is calcified due to inflammation in it or degenerative damage. Suddenly you cannot move your shoulder well without a specific reason. As you try not to use the arm in pain, you are likely to grab things with the other arm.
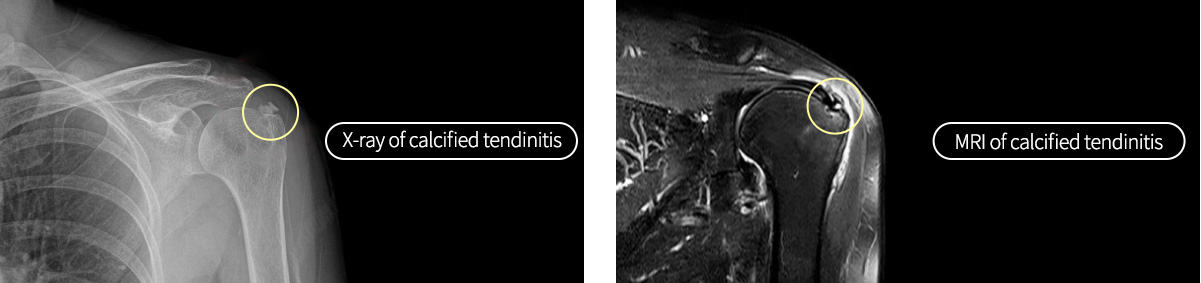
Treatment of calcific tendinitis
Treatments for calcific tendinitis can vary depending on where and when it appears. As long as the calcification is small, treating just inflammation can be helpful instead of removing the lime in the tendon.
-
Non-surgical treatment
Either medication, injection therapy, or physical therapy can be applied to the painful areas. The extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) breaks up calcified deposits in the tendon with a strong shock wave and stimulates the damaged tissue to heal.
-
Arthroscopic surgery
The pain disappears immediately after the calcified deposits are removed through the shoulder arthroscopy.
Shoulder arthritis
Like the knee, the shoulder also undergoes degenerative changes, in which its articular cartilage wears out with age and develops into arthritis. When the cartilage that covers the shoulder blade is worn out for various reasons and the joint capsule hardens, it is difficult for you to lift the arm with pain followed. Eventually it leads to movement disorders. On X-ray examination, you can see that the joint surface is irregular and hardened as the shoulder blades get tightly closer or abnormal osteophytes are formed.
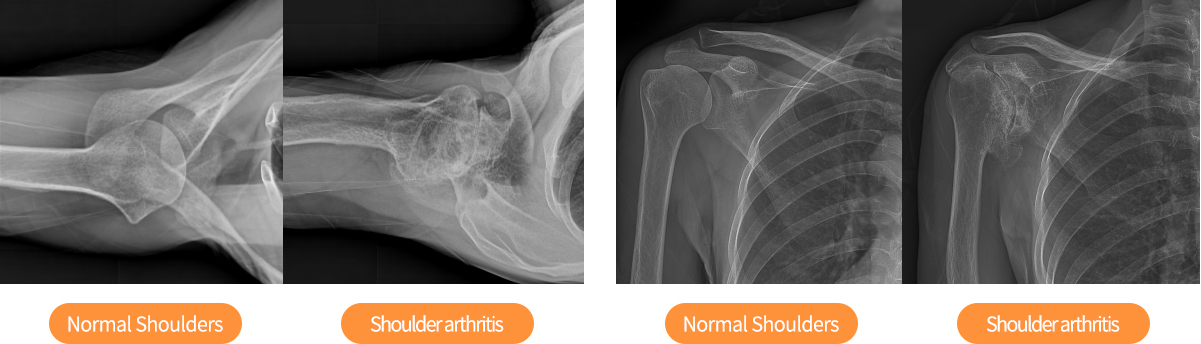
Treatment of shoulder arthritis
-
Non-surgical treatment
If symptoms are not severe, conservative treatment is preferred including exercise therapy, physical therapy, and injection therapy.
-
Arthroscopic surgery
Arthroscopy can be performed to remove unstable cartilage and remove its fragments to eliminate pain and prevent progressive cartilage damage.
-
Shoulder artificial joint surgery
In the terminal stage when the cartilage is damaged seriously and other treatments do not work any more, shoulder arthroplasty can be performed to replace the damaged shoulder joint with an artificial joint. Satisfying results can be expected with a certain level of exercise movement and pain relief.
*Rarely, there may be bleeding, infection, or blood clots during surgery.