Medical Information
Neurosurgery
- Orthopedic Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- General Surgery
- Pediatrics and Adolescents
- Emergency Medicine
- Kidney Medicine
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Respiratory Medicine
- Gastroenterology
- Family Medicine
- Neurology
- Gynecology
- Dental Clinic
- Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine
- Occupational Environmental Medicine
- Radiology
- Diagnostic Laboratory Medicine
Neurosurgery
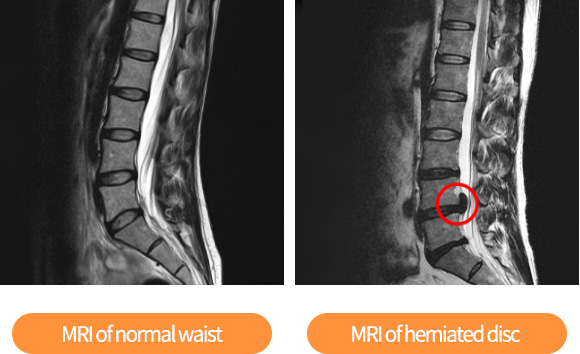
Herniated Lumbar Disc
The soft tissue that acts as a cushion between vertebrae is called an intervertebral disc. In the middle of the disc, there is a substance called nucleus pulposus made of protein, and a membrane called annulus fibrosus that surrounds nucleus pulposus. The nucleus pulposus is a soft tissue that contains a large amount of water. It is flexible and highly elastic. However, degenerative changes from aging or trauma can cause nucleus pulposus to protrude out of annulus fibrosus and press on the nerve, in which back pain occurs. This is called a herniated disc.
Symptoms of Lower Back Disc
Along with back pain, radiating pain or numbness in the legs occur.

Treatments of Herniated Lumbar Disc
-
Conservative Treatments
If the pain is not severe, medication, physical therapy, or injection therapy can be performed.
-
Non-surgical Treatments
● Nerve Blocks
A surgeon finds the nerve branch that causes pain and injects a medication to treat the pain.● Epidural Neuroplasty
It is a procedure that finds the cause of pain by inserting a 1mm small catheter and resolves nerve adhesion. Performed under local anesthesia, it gives little stress to a patient. You can go back to your daily life immediately after the procedure without hospitalization.● Nucleoplasty
A surgeon inserts a thin needle less than 1mm diameter into the disc and shoots high-density ions to break down the complex molecules in the disc that compress the spinal nerves. After the molecules turn simpler, they are coagulated. Performed in an outpatient setting less than 30 minutes, it allows you to go back to your daily life immediately. -
Surgical Treatments
● Endoscopic Spine Surgery
A surgeon removes the disc while checking directly through the monitor and inserting an endoscope and surgical instruments into a 5~8mm hole. It is safe as normal tissues can be accurately distinguished from lesions. A surgeon can treat them with confidence, and reduce risk of surgery.● Microdiscectomy
Normal tissues can be saved as much as possible and ruptured disc can be removed with a small incision of 0.5 cm. Using a microscope that magnifies the surgical area 10 to 20 times, a surgeon can secure his/her vision. It is safe and minimizes the size of incision.
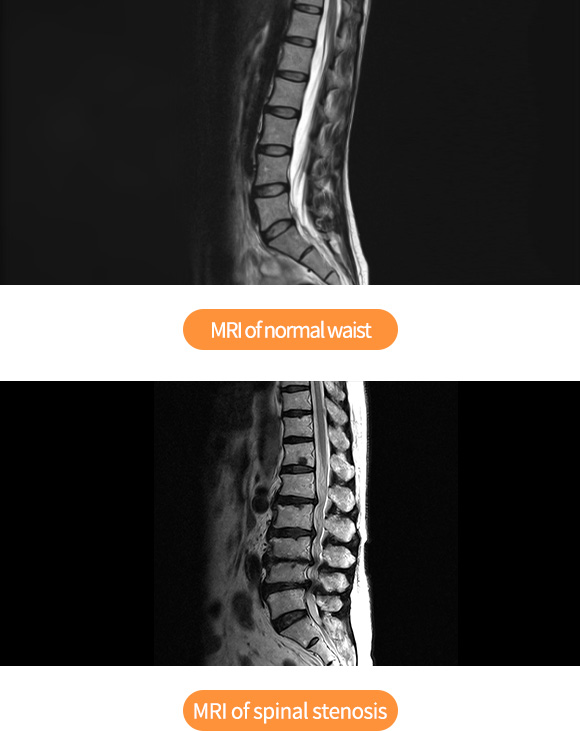
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a disease in which the spinal canal that protects nerve bundles is narrowed down for some reasons and compresses nerves. Most spinal stenosis are acquired as the spinal canal is closed up with age. Due to degenerative changes, ligaments and joints at the back of the spinal canal gradually become larger, after which nerve pathways become narrow and then pain occurs.
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
The pain starts from the back and buttock, the thigh gradually gets strained, and you may feel severe pain in the leg while you walk. As it is too painful, you cannot continue to walk.

Treatments of Spinal Stenosis
-
Conservative Treatment
• There is no need for surgery as long as it does not interfere with your daily activities. Exercise therapy is the most effective to slow down stenosis of spinal canal with aging.
• At the early stage, conservative treatment including selective injection therapy, physical therapy, and exercise therapy can be effective. -
Non-Surgical Treatments
● Epidural Neuroplasty
It is a procedure that finds the cause of pain by inserting a 1mm small catheter and resolves nerve adhesion. Performed under local anesthesia, it gives little stress to a patient. You can go back to your daily life immediately after the procedure without hospitalization.● Balloon Dilatation
This is a treatment to widen a nerve passage, in which a surgeon inserts a thin tube (special catheter) with a built-in balloon into the intervertebral foramen, a narrowed spinal nerve passage, followed by inflating the balloon. This procedure has been certified for safety and effectiveness by the Ministry of Health and Welfare. Those who have not been able to take benefits from nerve injection therapy or nerve blocks and those who suffer from intractable spinal stenosis can see the pain reduced. -
surgical treatment
● Microscopic Decompression
While a surgeon makes a minimal incision on the back and magnifies the lesion area with a microscope, he/she removes the lesion after partially removing the thickened bones and ligaments that compress nerves with his vision secured on the other side as well. There is little damage to nerves or surrounding muscles. You can recover fast enough to walk the next day without almost any pain.● Spinal Fusion
This is a treatment that removes bones, ligaments, and protruding discs that have undergone degenerative changes. A surgeon inserts artificial bones for spinal fusion and fixes it with screws so that the spine does not move.
This treatment provides firm stability to the spine and relieves pain effectively.
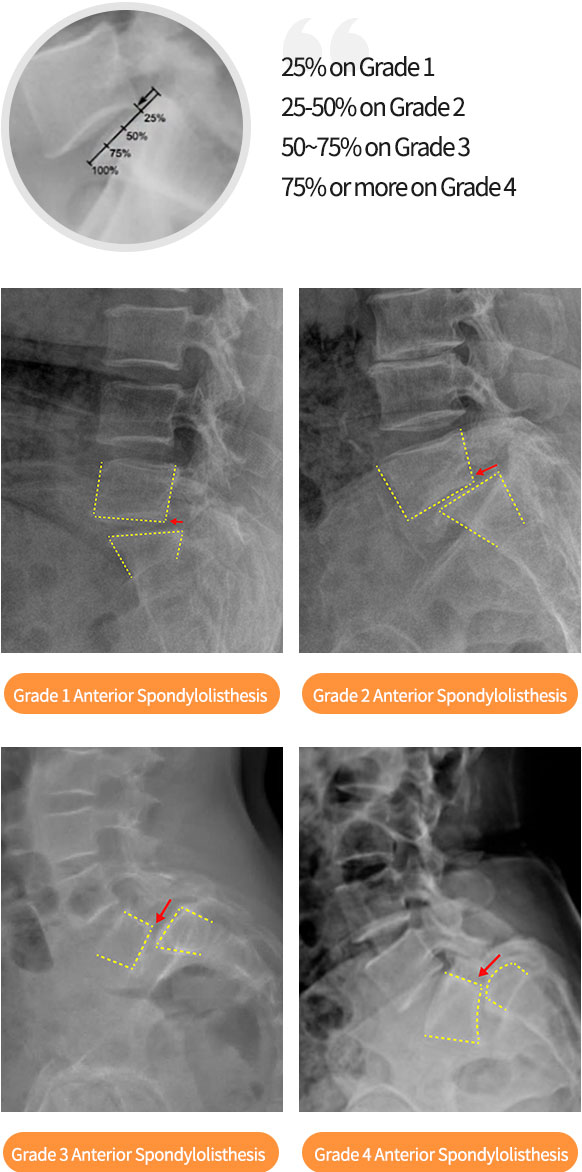
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which the connected vertebral nodes are separated due to various factors including strong external shocks or degenerative changes, and the upper bone of the separated part slips out of place onto the vertebra below it.
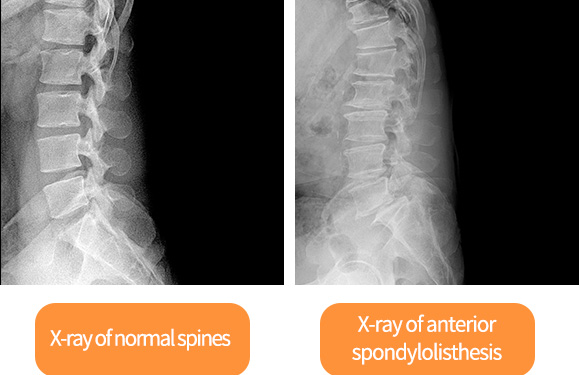
Diagnosis of Spondylolisthesis
It can be diagnosed easily with X-ray examination. Depending on the level of protrusion, it can be divided into stage 1, 2, 3, or 4.
Treatments of Spondylolisthesis
-
Conservative Treatments
At the early stage, it is critical you rest in the bed and restrict physical activity. You should take some painkillers and wear orthosis.
-
Epidural Neuroplasty
This is a procedure that finds the cause of pain by inserting a 1mm small catheter and resolves nerve adhesion.
Performed under local anesthesia, it gives little stress to a patient. You can go back to your daily life immediately after the procedure without hospitalization. -
Spinal Fusion
It is a surgical procedure to fix unstable deformed vertebrae with screws and make them sturdy.
With advanced technology of spinal fixation, you can start to walk in 1 to 2 days after surgery and recurrence rate is low.
Spinal Compression Fracture
Vertebral compression fracture happens when an external shock causes damage. Osteoporosis is usually the common cause of the fracture. When the front part of the vertebrae is distorted and damaged, it is called a compression fracture. It causes severe pain in the lower back as well as mere fracture. Once a compression fracture occurs, another one may follow. If left untreated, the spine can be deformed, which can cause the lower back to be bent gradually.
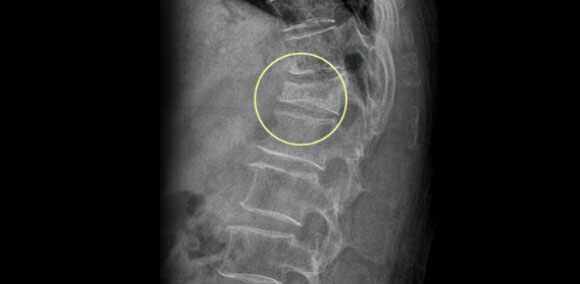
Treatments of Spinal Compression Fracture
-
Conservative Treatments
In case of minor fracture, a conservative treatment can be applied that you should take some painkillers and wear orthosis.
-
Bone Cement Vertebroplasty
This is a surgery in which a specially designed liquid bone cement is injected by inserting a long needle into a broken or collapsed vertebra. It is to restore the vertebrae to its original healthy state. A partial anesthesia allows seniors to take this treatment and gives little risk to those who are concerned about complications.
Internal Derangement of Disc
It happens when the properties of the disc are changed or the fibers surrounding nucleus pulposus are damaged, causing back pain. While a herniated disc compresses nerves after the disc protrudes, the internal derangement causes chronic pain as the biggest problem as the disc itself is damaged.
Scoliosis
If you have scoliosis, your spine bends toward left or right. A normal spine has an S-shaped curve when viewed from the side and straight from the front. It is diagnosed as scoliosis when the spine is bent sideways as viewed from the front.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a disease in which the lower back stiffens after the spine has inflammation. It occurs usually to young men. While the exact cause is unknown, it is said to be related to a gene called HLA-B27.
* In rare cases, bleeding, infection, and blood clots may occur during surgery.


